Understanding ICRA and Determining Your Project's Risk and Precautions
What is ICRA?
The Infection Control Risk Assessment (ICRA) is a critical tool used in healthcare construction and renovation projects to minimize the risk of infection for patients, staff, and visitors. It evaluates potential hazards and determines the necessary precautions to maintain a safe environment during construction.
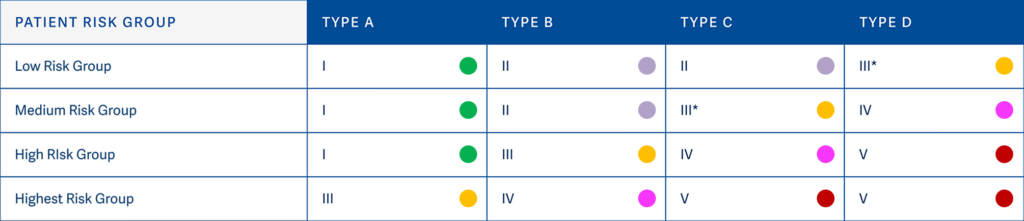
The latest version, ICRA 2.0, provides a structured matrix to identify the appropriate infection control measures based on two key factors:
- Construction Project Type
(e.g., demolition, minor repairs, renovations) - Patient Risk Group
(e.g., low-risk patients, high-risk immunocompromised patients)
By intersecting these factors in the ICRA 2.0 matrix, you can determine the Class of Precautions required and the surrounding area assessment needed to safeguard health.

Using the ICRA 2.0 Matrix
To effectively implement ICRA 2.0, follow these five essential steps outlined by the American Society for Healthcare Engineering (ASHE). For detailed guidance, refer to the ASHE ICRA 2.0 Tool and Permit Guide.
1. Identify the Construction Project Type
Classify your project as Type A, B, C, or D based on the scope of work and its potential to generate dust, disturb airflow, or impact healthcare operations.
2. Determine the Patient Risk Group
Assess the vulnerability of nearby patients by identifying the risk group (Low, Medium, High, or Highest Risk) based on their medical needs and immune status.
3. Use the Matrix
Cross-reference your project type with the patient risk group in the ICRA 2.0 matrix to establish the required Class of Precautions.
4. Surrounding Area Assessment
Evaluate the impact on adjacent areas (e.g. airflow, HVAC) to ensure barriers, containment, and mitigation measures align with the matrix’s recommendations.
5. Minimum Required Actions
Implement essential infection control measures like barriers, HEPA filtration, or negative air pressure according to the precautions class.

By following these steps, you can ensure compliance with infection control standards and minimize the risk of healthcare-associated infections during construction or renovation projects. Keep an eye out for more Best Practice articles in the future, where we’ll share additional insights to help you navigate healthcare construction projects with confidence!
